Aseptic compounding is a specialised skillset that is needed by healthcare staff, such as pharmacists, pharmacy technicians and nurses, who are required to prepare medication for patient use. The process involves aseptic techniques, which apply strict rules in practices and procedures to prevent the medicinal products from being contaminated with pathogens, in order to minimise the risk of infections. Aseptic compounding is an essential service as it provides preparations to patients for whom there are no commercially available options.
In order to produce highly trained healthcare personnel in this area to provide system benefits of safety, quality and efficacy of sterile drug compounded products, the Pharmaceutical Society of Singapore (PSS) has been conducting an annual Aseptic Compounding Course for pharmacists and pharmacy technicians to cater towards national competency standards. Various hospital institutions send their healthcare staff working in the area of aseptic compounding to this course which comprises of a combination of online learning methods (e.g. e-lectures, video demonstrations and interactive exercises) and online facilitated discussions. However, hands-on practical training typically takes the form of on-the-job training (OJT) by the relevant hospital institution, under the supervision of experienced staff. In general, it takes between 3 to 6 months before a learner can function independently.
There are several challenges that have been identified by trainers and learners in this field. There is an educational gap in practice as there is a lack of consistency in training and assessment practices among different hospital institutions. Furthermore, variations in training preferences and techniques among trainers tend to lead to confusion among learners when they practice. In addition, it is difficult to train and assess healthcare staff in the practical aspects of aseptic compounding due to the limited number of experienced trainers, facilities (e.g. cleanrooms) and equipment (e.g. laminar flow cabinets). At most times, hospital institutions can only conduct the hands-on training in their own cleanrooms during operational/working hours, which results in workflow disruptions and increase in waiting times since the time cannot be used to prepare actual products for patients.
The current physical training environment cannot be replicated to cater for all learners, which impacts on the clarity of understanding and accurate interpretation of protocols by the learners. Therefore, in order to address the above-mentioned challenges, there is a need to create a standardized hands-on training and assessment program that allows learning and practice outside of physical facilities.
As part of a competitive learning innovation grant challenge, called InnovPlus, organised by inlab of the Institute for Adult Learning (IAL), our team (code-named CAPSULE, Figure 1) was awarded a grant to develop a Virtual Aseptic Compounding (VAC) training and assessment program to provide standardized hands-on practice of aseptic compounding in an authentic laboratory environment. The InnovPlus grant challenge awards up to $200,000 to winning organizations to explore, innovate, develop and trial innovative solutions that advance Continuing Education and Training (CET) practice and outcomes, and is run twice a year.
Figure 1. Members of Team CAPSULE.
The VAC program will utilize advanced gaming technology to create a mixed reality simulation game that mimics the clean room environment. Combined with artificial-intelligence (AI)-based algorithms and three-dimensional (3D)-printed tools, the platform will track the tasks completed by learners and match the game interaction data with real-world competency standards, in order to discover the learners’ gaps and proficiencies. Our pedagogical approach (Figure 2) will combine evidence-centered gamification and educational frameworks that situate learning tasks in the context of real-world situations, so as to allow learners to experience the same problem-solving challenges in the training curriculum as they do in their daily endeavours. In particular, as part of this project, we will develop a set of Entrustable Professional Activities (EPAs) for aseptic compounding for use at a national level.
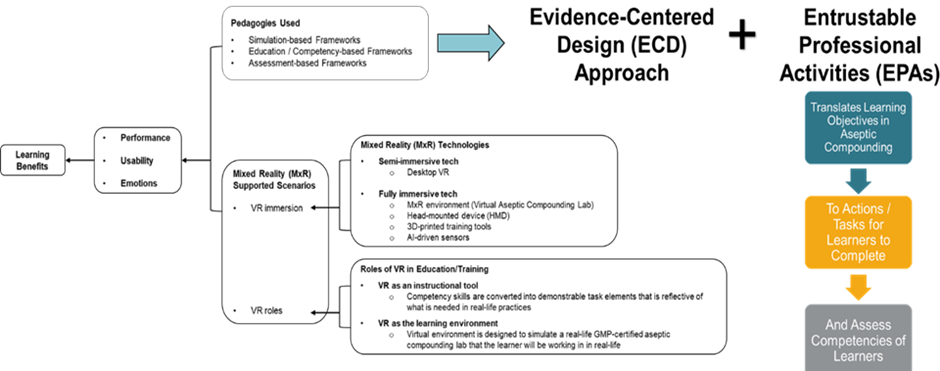
Figure 2. Summary of the pedagogies used to develop the VAC program.
The VAC aims to provide standardized and structured hands-on practical training, so as to strengthen national competency standards and best practices. We hope that this program can contribute to aseptic compounding manpower development at a larger scale in the near future to meet the demands of the centralized sterile drug compounding hubs which are a part of the National Pharmacy Strategy. This workforce will also play a role in mitigating the impact of future nationwide drug shortages resulting from any possible future disease pandemics.
CAPSULE Team Members:
Ms Ng Cheng Li (Department of Pharmacy, KKH, Trainer for the PSS Aseptic Compounding Course), Dr Tsang Wing Yee (Department of Pharmacy, SGH), Ms Jacelyn Han (Department of Pharmacy, SGH), Ms Petrina Fan (Department of Pharmacy, SGH), Ms Shakunthala D/O Hans Raj (Department of Pharmacy, SGH), Dr Kevin Yap (Department of Pharmacy, SGH), Mr Ivan Boo (INMEET CMS Pte Ltd)
Authored by Dr Kevin Yap (Department of Pharmacy, SGH)


